Spectrum is for telecommunication what jet fuel is for aviation. Spectrum is a range of electromagnetic frequencies or airwaves that telecom companies use for establishing a connection between a cell tower and a mobile phone. The bandwidth of this spectrum is directly proportional to the speed of a wireless data network (since more data can be transmitted simultaneously through a broader data pipeline). In contrast, the frequency is inversely proportional to the coverage (since lower frequencies penetrate better through physical barriers and thus have wider coverage).
The spectrum holding data sheet embedded in this article represents the current spectrum holdings of all active telecom operators across all frequency bands across all 22 telecom circles along with their liberalisation status and expiry dates. All figures represented are in MHz. The value mentioned in the bracket beside the frequency at the base of each sheet is the band number where ‘B’ stands for 4G LTE band whereas ‘n’ stands for the corresponding 5G NR band.
The spectrum shown under BSNL and Aircel in white is reserved for the respective operators but has not yet been officially allotted to them.
Spectrum Liberalisation:
Spectrum was administratively allocated to operators in each of the 22 licensed service areas or circles prior to 2010, this spectrum is called non-liberalised and can only be used for 2G services whereas all airwaves allotted post-2010 have been through a Spectrum Auction where operators have paid the market discovered price and this spectrum is called liberalised and can be used for any technology platform 2G/3G/4G/5G. Alternatively, operators may choose to liberalise their administratively allotted spectrum by paying the market-discovered price to DoT on a pro-rata basis for the remaining validity of the spectrum.
Paired and Unpaired spectrum:
Spectrum may be paired or unpaired, bands 1/3/5/8/28 are all paired where one set of frequencies is used for uplink whereas another distinct set of frequencies is used for downlink known as Frequency-division duplexing (FDD), whereas bands 40/41/78/258 are unpaired where both uplink and downlink happens in the same set of frequencies separated by the time of uplink and downlink known as Time-division duplexing (TDD).
List of Indian FDD Bands:
| 4G LTE band | 5G NR band | Uplink frequency range (MHz) | Downlink frequency range (MHz) | Bandwidth for telecom (MHz) | Block size (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | n1 | 1939-1979 | 2129-2169 | 40×2 | 5×2 |
| B3 | n3 | 1710-1780 | 1805-1875 | 70×2 | 0.2×2 |
| B5 | n5 | 824-844 | 869-889 | 20×2 | 1.25×2 |
| B8 | n8 | 890-915 | 935-960 | 25×2 | 0.2×2 |
| B28 | n28 | 723-733/ 738-748 | 778-788/ 793-803 | 20×2 | 5×2 |
List of Indian TDD Bands:
| 4G LTE band | 5G NR band | Frequency range (MHz) | Bandwidth for telecom (MHz) | Block size (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B40 | n40 | 2300-2380 | 80 | 10 |
| B41 | n41 | 2535-2555/ 2615-2655 | 60 | 10 |
| – | n78 | 3300-3670 | 370 | 10 |
| – | n258 | 24250-27500 | 3250 | 50 |
Spectrum caps:
A spectrum cap dictates how much spectrum a particular operator can hold in a circle for a specific band. There is a 40% cap for Sub-GHz spectrum in the 700/850/900 MHz bands combined, a 40% cap for Mid-Band spectrum in the 1800/2100/2300/2500 MHz bands combined, a 40% cap for the C-Band spectrum of 3300-3670 MHz and a 40% cap for the mm-Wave spectrum bands of 24.25-27.5 GHz. The current spectrum caps are denoted in the spectrum chart.
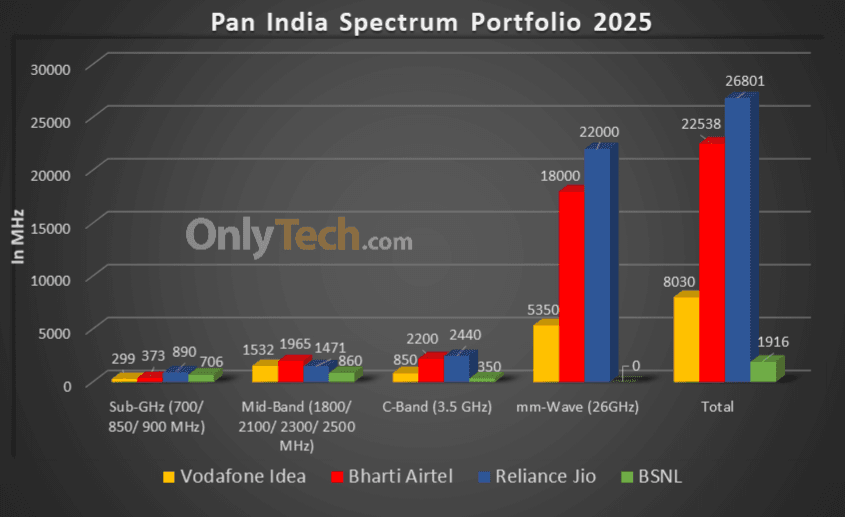
Overall spectrum holdings of operators (in MHz):
| Operator/Holding | Jio | Airtel | Vi | BSNL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-GHz | 890 | 373.2 | 298.8 | 706 |
| Mid Band | 1470.8 | 1964.9 | 1531.6 | 860 |
| C-Band | 2440 | 2200 | 850 | 350 |
| mm-Wave Band | 22000 | 18000 | 5350 | 0 |
| Total | 26,800.8 | 22,538.1 | 8,030.4 | 1,916 |
Spectrum sharing/trading/leasing guidelines:
- Telecom operators holding CMTS/UASL/UL licenses can enter into a Spectrum-Sharing agreement with each other so long as both parties hold liberalised spectrum in the same band in the same circle. Spectrum sharing is possible only on a Pan LSA level in block sizes defined by DoT and only after one year of an operator acquiring the spectrum.
- Telecom operators holding CMTS/UASL/UL licenses can enter into a Spectrum-Trading agreement with each other so long as the spectrum being sold is liberalised. Trading of spectrum is possible only on a Pan LSA level in block sizes defined by DoT and only after two years of an operator acquiring the spectrum.
- Telecom operators may enter into a Spectrum-Leasing agreement only with Enterprises holding a Captive Non-Public Network (CNPN) license and not with each other. The lease may be limited to any geographic area within the LSA and for any duration mutually agreed upon by both parties. A CNPN licensee can lease spectrum from multiple operators within an LSA.
Note: We update this chart in real-time to ensure it is always up to date with the latest changes in spectrum holding. Certain human errors might have crept in during the manual compilation of the data, any mistakes/ rectification can be brought to the Team’s notice through the comments section below.







In any direction I saw a jio tower exist. Even on Tarang sanchar portal there are many many jio tower. Even airtel, vi and BSNL combined doesn’t have that much of tower. Where it is city, highway or village everywhere it is. IS IT SO BECAUSE JIO HAD THE LEAST AMOUNT OF SPECTRUM ? Even then airtel and vi offers better speeds than jio.
@esmail why same band say Band1 coverage decrease when used for 4G than 3G
@Esmail: Yes I have also noticed, 900 mhz (Band 8) 2G has more coverage than 900 mhz (Band 8) 4G. Can you please explain why is this so ???
I guess so May be it is related to power used by BTS ?
@Esmail: Your comments on this ???
As far as I can reckon, this would have to do with the load on a particular network at any given time. Mobile towers have the dynamic ability to adjust the transmission power to control the coverage of a network based on the load on the network. So if too many users are connected to a tower and are using the network bandwidth aggressively then the tower will reduce the transmission power to reduce the coverage radius, thus shedding off the users which are at the distant periphery of the network so as to focus that bandwidth towards serving the users who are closer to the tower. The reverse is also true, which is why people who live far from mobile towers may notice better signal strength in the late night and early mornings when the usage is less.
Now for the difference in coverage radius of 2G and 4G networks on the same spectrum band, if we apply the same logic of dynamic control of transmission power based on network load, 4G uses way more bandwidth compared to 2G which is mainly used for carrying voice traffic, thus the same spectrum bandwidth can serve way more 2G users than it can for 4G users. Thus the lower coverage for 4G network compared to 2G network on the same spectrum band.